Jump to topic
Search
Program Details
The Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship is a well-established advanced fellowship program, providing fellows with state-of-the-art training in all aspects of heart rhythm management.
The ACGME-accredited program is designed to meet all of the requirements for board eligibility in Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology and provides level 3 COCATS training in clinical electrophysiology, ablation and device implantation and follow-up. A continuity outpatient experience in the arrhythmia clinic, along with arrhythmia consultation of a diverse arrhythmia population, including postoperative arrhythmias, arrhythmias from patients on a busy congestive heart failure/cardiac transplant service, and an adult congenital heart disease program is emphasized. Trainees are exposed and can participate in clinical and basic research. Research emphasis is on clinical trials involving investigational antiarrhythmic drugs and implantable devices.
Learn More About the Fellowship
Application Overview
All applications must be submitted through ERAS, and the program participates in the National Residency Matching Program (NRMP). Applications will not be received outside of ERAS, and positions will not be filled outside the match.
Application deadline is July 24, 2024.
Eligibility
Qualified candidates will be:
- U.S. citizens, permanent residents or J-1 visa holders (no additional visa types are sponsored)
- Board-eligible or board-certified in internal medicine
- Pennsylvania medical training license eligible
Required Supporting Documents
The following documents should be uploaded to ERAS for review:
- ERAS application, inclusive of current photograph
- Personal statement
- Curriculum vitae
- USMLE or COMLEX transcript
- ECFMG certificate (if applicable)
- Letters of recommendation – minimum 3-4 letters, including one from current program director
Interview Process
Thank you for your interest in our program. Interviews are expected to take place virtually for 2024; however, this is subject to change, and we encourage you to check back often.
Interview dates for 2024 will be:
- Sept. 9
- Sept. 13
- Sept. 30
- Oct. 7
- Oct. 10
- Oct. 25 (tentative)
All interviews are by invitation only and will be scheduled through Thalamus.
Virtual Tour
Penn State Health
Penn State Health is an integrated academic health system serving patients and communities across 15 counties in central Pennsylvania. It employs more than 20,900 people systemwide.
The system includes Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Penn State Health Children’s Hospital and Penn State Cancer Institute based in Hershey, Pa.; Penn State Health Hampden Medical Center in Enola, Pa.; Penn State Health Holy Spirit Medical Center in Camp Hill, Pa.; Penn State Health Lancaster Medical Center in Lancaster, Pa.; Penn State Health St. Joseph Medical Center in Reading, Pa.; Pennsylvania Psychiatric Institute, a specialty provider of inpatient and outpatient behavioral health services, in Harrisburg, Pa.; and 2,417 physicians and direct care providers at 225 outpatient practices. Additionally, the system jointly operates various healthcare providers, including Penn State Health Rehabilitation Hospital, Hershey Outpatient Surgery Center and Hershey Endoscopy Center.
In 2017, Penn State Health partnered with Highmark Health to facilitate creation of a value-based, community care network in the region.
Penn State Health shares an integrated strategic plan and operations with Penn State College of Medicine, the University’s medical school. With campuses in State College and Hershey, Pa., the College of Medicine boasts a portfolio of more than $150 million in funded research and more than 1,700 students and trainees in medicine, nursing, other health professions and biomedical research.
Learn more about Penn State Health
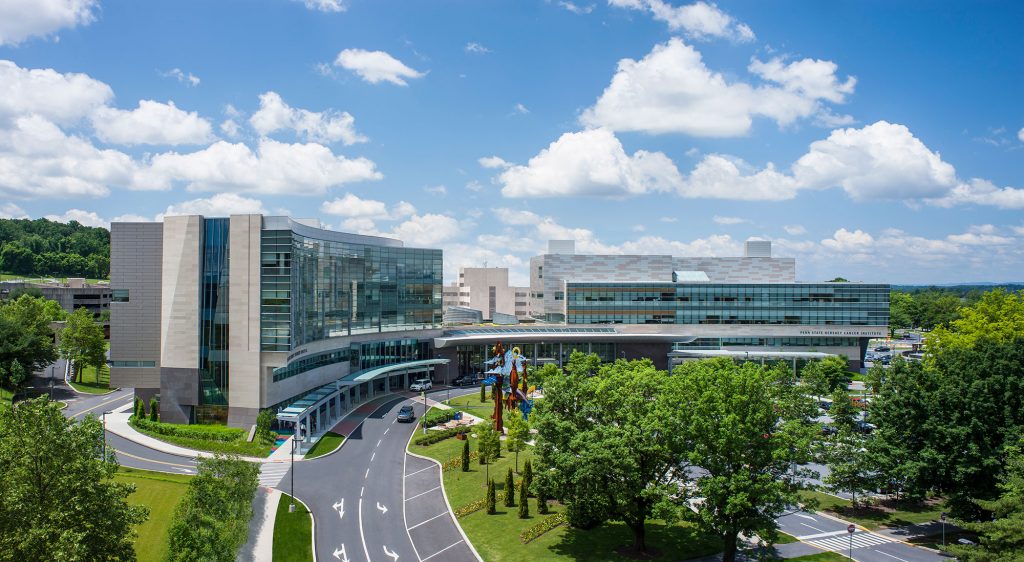

Penn State Health Children’s Hospital (left), Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center (center) and Penn State Cancer Institute (right)
Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center
500 University Dr., Hershey, Pa., 17033 (Derry Township, Dauphin County)
- The health system’s 611-bed flagship teaching and research hospital
- The only medical facility in Pennsylvania accredited as both an adult and a pediatric Level I (highest-level) trauma center
- Dedicated surgical, neuroscience, cardiovascular, trauma and medical intensive care units
- Accredited Life Lion critical-care transport providing more than 1,100 helicopter and approximately 750 ground ambulance transports per year
- More than 1,300 faculty members and more than 650 residents and fellows
- Approximately 29,000 admissions, 73,000 emergency department visits, 1.1 million outpatient visits and 33,000 surgical procedures annually
- Designated as a Magnet hospital since 2007
Learn more about Milton S. Hershey Medical Center
Penn State Health Children’s Hospital
600 University Dr., Hershey, Pa. 17033 (Derry Township, Dauphin County)
- An eight-story, 263,000-square-foot-facility built in 2013 and expanded in 2020
- 160 licensed pediatric beds, 26-bed pediatric intensive care unit and a 56-bed neonatal intensive care unit
- Level IV (highest-level) neonatal intensive care unit
- Level I quaternary (highest-level) pediatric intensive care unit
- Level I (highest-level) pediatric trauma center designation
- Intermediate care unit
- Dedicated pediatric operating rooms
- More than 150,000 pediatric outpatient visits, 20,000 pediatric emergency room visits, and approximately 5,000 pediatric patient discharges annually
Welcome to Hershey
More About Hershey
Interested in learning more about living and working in Hershey, Pa.? See details here:
Wellness, including emotional, spiritual, social and physical health, is a crucial component to training and to becoming a professional, compassionate and resilient physician. Self-care is a skill which must be continually practiced and reinforced. Penn State College of Medicine and Penn State Health are committed to addressing wellness among residents and fellows, with multiple resources readily available.
Institutional resources
- Visit BeWell – a health program designed to support Penn State Health employees
- See Penn State College of Medicine wellness resources here
- Employee Health Care Concierge and Case Management Service
- Partners in Medicine
Moving to a new city with your family does not have to be stressful. Residency programs have assisted many significant others with finding employment. There is also a GME-Wide Partners in Medicine (PIM) group that offers networking opportunities as well as various social and community oriented activities. - The Doctors Kienle Center for Humanistic Medicine
- Active and easily accessed Office of Professional Mental Health
Graduate medical education resources
Institutional Resources
Penn State Health and Penn State College of Medicine celebrate, embrace and support the diversity of all patients, faculty, staff, students and trainees.
Office for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
In keeping with this, Penn State Health has an active Office for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion with various programs, networks and resource groups, including:
- Talks and lectures on diversity, equity and inclusion through the Inclusion Academy
- Regular events on topics such as eradicating racism and creating a culture of inclusiveness
- Many Business Employee Resource Groups (BERGs), including:
- Disability Business Employee Resource Group
- Interfaith Business Employee Resource Group
- LGBTQ+ Business Employee Resource Group
- Military and Veterans Business Employee Resource Group
- Multicultural Business Employee Resource Group
- NextGen Business Employee Resource Group
- Black Physician Professional Staff Association – Resource Group
- Hispanic Professional Association
- Asian Physician and Professional Staff Association
- International Workforce Inclusion
- Inclusion Academy
Learn more about the Penn State Health Office for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
Learn more about the College of Medicine’s Office for Diversity, Equity and Belonging
Office for Culturally Responsive Health Care Education
The vision at Penn State College of Medicine and Penn State Health is to equip learners with the knowledge, skills and attitudes they will need to provide culturally excellent health care and research for an increasingly diverse U.S. population. The Office for Culturally Responsive Health Care Education was formed to help meet that goal.
Learn more about the Office for Culturally Responsive Health Care Education
Office for a Respectful Learning Environment
In addition, the institution does not tolerate discrimination, biases, microaggression, harassment or learner mistreatment of any kind, and any concerns are immediately addressed by the Office for a Respectful Learning Environment.
Learn more about the Office for a Respectful Learning Environment
Network of Under-represented Residents and Fellows
The Network of Under-represented Residents and Fellows (NURF) is a group of diverse residents and fellows representing all specialties. NURF’s goal is to promote cultural diversity in the residency programs through community involvement, mentorship with diverse faculty, professional networking and support for the recruitment of diverse medical students into the residency programs.
NURF is sponsored by the Penn State College of Medicine Graduate Medical Education Office and the Penn State Health Office for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion.
Leadership

Amanda Cai, MD
Faculty Leader
Dorothy Jung, MD
Fellow Leader
Overview
Women in Cardiology:
- Strives to foster a supportive environment for women in Cardiology and its subspecialties at Penn State Hershey Medical Center
- Offers unique opportunities to address and support career-focused education for women within our field
- Provide resources for leadership, mentoring and families
- Minimum of bi-annual events for participation
- Attending and fellow-level support system

Mailing Address
Penn State Heart and Vascular Institute
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship Program
500 University Drive
P.O. Box 850, MC H047
Hershey, PA 17033
General Contact Information
Phone: 717-531-6746
Curriculum Details
The goal of the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Program is to train fellows who:
- Have a broad knowledge of the total spectrum of arrhythmias, both supraventricular and ventricular tachyarrhythmias, as well as bradyarrhythmias.
- Have an advanced knowledge base in basic clinical cardiac electrophysiology and pharmacology.
- Are adept in interpreting complex electrocardiology and able to provide expert consultative care for patients with arrhythmias.
- Are familiar and proficient with the indications and safe use of invasive electrophysiology procedures.
- Are capable of independently performing and analyzing both noninvasive and invasive electrophysiologic tests.
- Have participated in, and are able to critically analyze research pertaining to electrophysiology.
- Provide compassionate and state-of-the-art care to their patients with arrhythmias.
Fellows will fulfill the suggested guidelines for training as outlined in the 2015 Advanced Training Statement on Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society. As described in this document, fellows are expected to achieve Level III training in performing, interpreting and training others to perform and render advanced, specialized arrhythmia care. Fellows will meet these requirements during the course of the two-year CCEP fellowship. Prior procedure volumes during Levels 1 and 2 training can be counted towards total Level 3 training numbers.
Level 1: Two months
- 10 temporary pacemakers
- 10 cardioversions
Level 2: Six months
- 100 CIED interrogations/programming
Level 3: 12 to 24 months
- 150 or more electrophysiology cases
- 75 ablations
- 30 to 50 atrial fibrillation ablations
- 10 or more transseptal procedures
- 75 CEDs (25 ICD, 25 dual-chamber devices, 25 CRT devices)
- 30 CIED revisions/placements
- 200 CIED interrogation/programming (100 ICDS, 100 pacemakers)
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to train fellows to proficiently and safely implant devices in the appropriate patients.
Objectives
By the end of four months, the fellow should:
- Understand the indications for implantation of ILRs (implantable loop recorders), pacemakers, ICDs and resynchronization devices. (PC,MK)
- Be able to discuss with the patient the indication for their device, the procedure, risks and benefits. (PC, MK, ISC,P, SBP)
- Know the co-morbid factors that increase the risk of the procedure planned. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Assist or perform, with supervision, an uncomplicated pacemaker or ICD implant, including pocket formation, vascular access, RA and RV lead placement and pocket closure. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Assist or perform an uncomplicated generator change. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Identify acceptable implant parameters, including pacing and sensing thresholds, and impedance. (PC, MK)
- Assist in defibrillation threshold testing and understand what an acceptable threshold is. (PC, MK)
- Assist in the placement of a coronary sinus lead. (PC, MK)
- Perform, with supervision, the placement of an ILR. (PC, MK)
- Assist in the management of conscious sedation. (PC, MK, P, SBP, ISC)
By the end of eight months, the fellow should:
- Perform, with supervision, an uncomplicated pacemaker or ICD implant. (PC, MK)
- Assist or perform, with supervision, a pacemaker or ICD revision, including pocket revision and/or lead revision. (PC, MK)
- Perform, with supervision, the placement of a coronary sinus lead. (PC, MK)
- Oversee the management of conscious sedation. (PC, MK, P, SBP, ISC)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be able to independently perform a pacemaker or ICD implant, including coronary sinus lead placement, and lead or pocket revision. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
At Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, pacemakers, ICDs, biventricular devices, and implantable loop recorders are implanted in a dedicated EP lab, which meets OR specifications. Surgeons do not participate in the cases, but are available for backup. Lead extractions are also performed. The EP fellow will participate in all of these cases.
Patients encompass a broad spectrum of ages and disease types, and the gender mix is appropriate. Most patients do have some form of insurance. Since Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center is a tertiary referral base for central Pennsylvania, the ethnicity of the patient population is fairly homogenous, although the socio-economic backgrounds are more diverse. Patients from the Lebanon VA are also referred for implant procedures. Due to the large number of patients with congenital heart disease and cardiomyopathies who are followed at the institution, many device patients are very complex and have severe underlying heart disease. Prior to implant, patients have either been evaluated as an outpatient in the clinic or as an EP consult in the hospital. Hospital transfers may be worked up in the observation unit adjacent to the EP lab.
- The fellow is responsible for evaluating and obtaining consent from all patients who will undergo a device implant (in cases which they will be participating).
- The fellow will review labs and other pertinent pre-op data and discuss the case with the EP attending prior to beginning the procedure.
- The fellow will participate as an assistant or primary operator, depending upon the complexity of the case and their stage of training.
- The fellow will place computer post-op orders and check post-op EKG and CxRs.
- The fellow will fill in data for computerized report and review with the EP attending.
- The fellow will follow the patient in recovery, monitoring for any potential complications.
- The fellow will keep a personal log of all their procedures that should be updated in New Innovations. Collected data should procedure description, indication, complications and supervising attending.
Qualified faculty is present for the entirety of every procedure. Fellows assume progressively increasing responsibility, according to their level of education, ability and experience. Before and after procedures, faculty can be reached easily and quickly. The fellow will review the case with the faculty member pre-op, and the attending and fellow will discuss the results of the case post-op.
The fellow is continuously being evaluated by the attending via the tutorial process. Every procedure they performs is overseen by the attending. Device implants are done concurrently with the other fellowship assignments, throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow receives written evaluations from each of the implanting EP attendings in the form of a procedural checklist every four months and a semi-annual general evaluation, both based on the ACGME core competencies. The EP program director discusses these evaluations with the fellow biannually. The fellow also receives 360-degree evaluations from patients and staff, providing feedback on communication skills and their professionalism. In turn, the fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing his evaluations. The fellow evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They also confidentially evaluate the attendings and EP program director.
Besides didactic sessions and self-study from educational materials, the fellow scrubs as the 1-degree operator on all his implant cases. The attending is also scrubbed and beside the fellow for the entire case, for instruction.
Didactic Sessions
- M and M (QI) Conference (EP and HVI)
- Core Curriculum Series
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Device Conference Series (Monthly) – sponsored by industry
- Instruction in programming and troubleshooting
- Outside courses sponsored by device companies or HRS, ACC
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to train fellows to appropriately and safely perform electrophysiologic procedures covering the total spectrum of arrhythmias, both supraventricular and ventricular tachyarrhythmias, as well as bradyarrhythmias. The fellow will develop expertise in catheter placement, programmed electrical stimulation, endocardial mapping, catheter ablation and interpretation of data.
Objectives
By the end of four months, the fellow should:
- Place all recording catheters for initial study with supervision. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Perform with supervision a basic diagnostic electrophysiology study. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Understand and be able to select appropriate diagnostic maneuvers in the assessment of supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Write a procedure report with supervision, including a discussion of the results. (PC, MK, PBLI, SBP, P, ISC)
- Assist in the mapping of tachycardias (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Understand concepts of electrogram selection in mapping. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Assist in transseptal catheterization. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Perform a cardioversion without supervision. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Assist in the management of conscious sedation. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC)
By the end of eight months, the fellow should:
- Be capable of performing a full diagnostic EP study with minimal supervision. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC)
- Be capable of teaching the basics of invasive diagnostic EP testing to a cardiology fellow. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC)
- Perform, with supervision, the mapping of tachycardias. (PC, MK, ISC, PBLI)
- Be capable of electrogram selection and interpretation, and use of 3-D mapping system. (PC, MK, ISC, PBLI)
- Perform transseptal catheterization with supervision. (PC, MK, ISC, PBLI)
- Oversee the management of conscious sedation. (PC, MK, ISC)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be capable of independently performing ablation procedures (with the exception of more advanced ablations, such as those for atrial fibrillation). (PC, MK, ISC, PBLI, SBP)
- Be capable of performing transseptal catheterization without supervision. (PC, MK, ISC)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
At Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, electrophysiology studies and ablations are done in a dedicated EP lab with dedicated EP trained staff. Cardioversions are performed in the EP or cath labs, as well as emergency department or intensive care units. Sedation is managed by the EP attending and fellow. The fellow participates in all EP procedures. As the fellow gains increasing proficiency over the course of training, they will gradually assume increasing independence.
Patients encompass a broad spectrum of ages and disease types, and the gender mix is appropriate. Most patients have some form of insurance. Since Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center is a tertiary referral base for Central PA, the ethnicity of the patient population is fairly homogenous, although the socioeconomic backgrounds are more diverse. Patients from the Lebanon VA Hospital are also referred for invasive EP procedures. A significant number of patients are referred by the congenital heart disease and heart failure groups. Therefore, many procedures involve patients with complex and severe underlying heart disease.
The fellows also participate in pediatric invasive EP procedures with a pediatric electrophysiologist. Prior to EP procedures, patients have either been evaluated as an outpatient in EP clinic or as an EP consult in the hospital. Hospital transfers are evaluated pre-procedure in the observation unit adjacent to the EP lab.
- The fellow is responsible for evaluating and consenting all patients who will undergo an EP study/ablation (in cases in which they will be participating).
- The fellow will review labs and other pertinent pre-op data and discuss the case with the EP attending prior to beginning the procedure.
- The fellow will participate as an assistant or primary operator, depending upon the complexity of the case and their stage of training.
- The fellow will place computer post-op orders and check post-op EKG and CxRs.
- The fellow will fill in data for computerized report and review with the EP attending.
- The fellow will follow the patient in recovery, monitoring for any potential complications.
- The fellow will keep a personal log of all their procedures. Collected data should include patient name, medical record number, date and time of procedure, indication, complications, and supervising attending.
Qualified faculty is present for the entirety of every procedure. Fellows assume progressively increasing responsibility, according to their level of education, ability and experience. Before and after procedures, faculty can be reached easily and quickly. The fellow will review the case with the faculty member pre-op, and the attending and fellow will discuss the results of the case post-op.
The fellow is continuously evaluated by the attending via the tutorial process. Every procedure they perform is overseen by the attending, who directly evaluates the fellow’s cognitive and technical skills. EP studies, ablations and cardioversions are done concurrently with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. Every four months, the fellow receives a written evaluation from each of the EP attendings in the form of a procedural checklist. Semi-annual general evaluations are also provided by each EP attending. All evaluations are based on the ACGME core competencies. The EP program director discusses the evaluations with the fellow. The fellow also receives a 360-degree evaluation from patients and staff, providing feedback on their communication and teaching skills, as well as their perceived professionalism. In turn, the fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They also confidentially evaluate the attending and EP program director.
Besides didactic sessions and self-study from the educational materials listed below, the fellow scrubs as the 1-degree operator. The attending is also scrubbed and beside the fellow for the entire case, for instruction.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conferences
- Core Curriculum Conference
- EKG Conference
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to train fellows to competently consult on patients with the entire spectrum of arrhythmia disorders.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Be competent in obtaining a full history with a focus on the pertinent facts pertaining to the question posed to the EP service. (PC, MK, ISC, P)
- Be capable of independently developing a differential diagnosis and diagnostic plan for the evaluation of clinical problems encountered in the hospital setting including: syncope, cardiac arrest, wide complex tachycardia, narrow complex tachycardia and bradycardia. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Be capable of acute management of clinical problems including cardiac arrest, wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response, and complete heart block, with minimal supervision. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC)
- Be capable of temporary transvenous pacemaker placement, with minimal supervision. (PC, MK)
- Perform, with supervision, the analysis and troubleshooting of pacemakers and ICDs. (PC, MK, ISC)
- Be capable of independent evaluation of telemetry strips and EKGs. (PC, MK)
- Be capable of discussing clearly and professionally with other physicians, staff, patients and their family the findings, opinions, and recommendations of the EP service. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be capable of independently providing inpatient EP consultation services. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Be capable of performing, without supervision, the analysis and troubleshooting of implantable devices. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
The EP consult team is asked to see inpatients with both “tachy” and “brady” arrhythmia problems. Patients are seen in the emergency department, medical and surgical ICUs, floor and telemetry units, and labor and delivery. The disease mix is both complex and varied, including patients who are pregnant, post heart or liver transplant, have congenital heart disease or being treated at Penn State Cancer Institute. There is an appropriate gender mix, and wide span of ages seen. The ethnicity of the patient population is fairly homogenous, but with diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Patients seen in consult may need electrical or chemical cardioversion, temporary or permanent pacing, or an EP study with possible ablation. A variety of noninvasive tests are also employed to aid in arrhythmia diagnosis.
- The fellow is responsible for seeing inpatient arrhythmia consults in a timely manner, and writing a consult note on the chart.
- The fellow will present the case to the EP consult attending, with whom an evaluation and treatment plan will be discussed.
- The fellow will obtain consent for any invasive EP procedure that is planned.
- The fellow will participate in any EP invasive procedures required for the consult patients they are following.
- The fellow will write follow-up note on the chart, if needed, to provide information on test results and revise recommendations.
- The fellow will assist in communicating with the primary team requesting the consult.
- The fellow will interact with the patient and the family, providing education and answering questions. The fellow will assume a bigger role in this duty as they progress in training.
The fellow will present each consult patient case to the EP attending at the bedside at which time the evaluation and treatment plan will be discussed. All EP procedures will be conducted with the EP attending present. In the case of an urgent or emergent consult, the EP attending will be in attendance with the fellow for the initial evaluation and to stabilize the patient.
EP consults are done concurrently with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The EP attendings are responsible for covering the EP consult service on a rotating basis and are able to directly assess the fellow’s progress over time. The fellow’s consultative skills are evaluated semi-annually by all EP attending. The evaluation used is based on the ACGME core competencies; the EP program director discusses the evaluations with the fellow. The fellow also receives 360-degree evaluations from patients and staff, providing feedback on their communication and teaching skills, as well as their perceived professionalism. In turn, the fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They also confidentially evaluate the attending and EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the EP attending and fellow. The fellow also learns by instructing general fellows, residents and medical students, as well as the patient and their family. Other important methods are self-study, and participating in the didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- EKG Conference
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to train fellows to skillfully approach patients referred for EP evaluation. They will be able to develop an appropriate assessment and plan for the new patients, and understand the appropriate follow-up for those with devices or needing antiarrhythmic drug therapy.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Obtain a full history, focusing on the pertinent facts relating to the EP question. (PC, MK, ISC, P)
- Be capable of independently developing a differential diagnosis plan. (PC, MK, PBLI, SBP)
- Be capable of independent evaluation of the results of outpatient monitoring and tilt table testing. (PC, MK)
- Be capable of discussing, clearly and professionally, the nature of the EP problem, as well as findings and recommendations, with the patient and referring physician. (PC, MK, ISC, P, SBP)
- Be capable of providing clear and professional documentation of patient office visits, results and plans in the medical records. (PC, MK, ISC, P, SBP)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be capable of independently assessing the continuing outpatient care of the EP patient, and adjusting their care as needed. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
The fellow may be assigned to outpatient continuity clinic at I.O. Silver Cardiovascular Specialties Clinic or the Nyes Road outpatient clinic. At each site, a wide range of noninvasive cardiac testing is available. Patients are referred and followed from a wide geographic region, including State College, Shamokin, Waynesboro, Wilkes-Barre and Hanover. The full spectrum of electrophysiological disorders are represented. There is an appropriate gender mix and adults of all ages are represented. Since the region represented is central Pennsylvania, the patient population is fairly homogenous, but with diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Patients may be referred for anti-arrhythmic drug therapy, ablation or device implant. Additionally, evaluation of syncope and palpitations is a common reason for referral.
- The fellow will attend his assigned continuity clinic half a day a week, which is supervised by an EP attending.
- The fellow will independently obtain the appropriate history, physician examination, interpret the EKG and other pertinent tests, and formulate an assessment and plan for new patients in the clinic.
- When an electrophysiologic procedure is planned, the fellow will discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with the patient.
- The fellow will dictate a letter documenting the office visit to the referring physician.
- The fellow will see the patient in clinic for follow-up post procedure, to provide continuity of care.
- The fellow will also see patients with chronic arrhythmia problems and participate in the decision-making regarding anti-arrhythmic drug therapy, as well as noninvasive testing.
- The fellow will discuss each patient seen with the attending electrophysiologist.
The fellow will discuss each patient they see in the clinic with the EP attending. The attending will also see the patient to confirm and help explain the findings and recommendations of the fellow.
Outpatient continuity clinic is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow is supervised in clinic by the same EP attending all year. The fellow’s clinical progress is observed on a weekly basis by the attending. The attending reviews and edits the fellow’s letters to referring physicians and provides feedback to the fellow. The fellow observes the attending physician’s interaction with patients in the clinic. The fellow is provided with immediate feedback during each case discussion with the attending. Additionally, the fellow receives written semi-annual evaluation from their clinic attending. This evaluation is based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellow also receives 360-degree evaluations from patients and clinic staff, providing feedback on communication skills and their professionalism. In turn, the fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing his evaluations. The fellow evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They also confidentially evaluate the attending and EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the EP clinic attending and fellow. The fellow learns by educating patients and their families. Other important methods are self-study, and participating in the didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- EKG Conference
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to train the fellow to competently follow pacemakers, ICDs, biventricular devices and implantable loop recorders. Additionally, they will learn to interpret and troubleshoot abnormal data, and program the appropriate prescription changes.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Understand the normal wound healing process after device implant, and discern when wounds are abnormal due to infection or hematoma. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Be able to interrogate and do simple reprogramming on all commonly used pacemakers and defibrillators. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Independently interpret telemetry data and measure pacemaker pacing and sensing thresholds. (PC, MK)
- Understand indications for device replacement. (PC, MK, SBP)
- With supervision, evaluate for lead malfunction. (PC, MK)
- With supervision, interpret stored intracardiac electrograms and delivered therapies. (PC, MK)
- With supervision, troubleshoot and make appropriate prescription changes to pacemakers and ICDs. (PC, MK)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Independently program appropriate prescription changes to devices based on patient symptoms, or abnormal telemetered/measured data. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Have mastered the techniques of device follow-up, reprogramming, indications for device replacement and evaluation of defective leads. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
The majority of patients with devices implanted at Hershey Medical Center are followed in the hospital–based device clinic. Follow-up of pacemakers, ICDs, biventricular devices and implantable loop recorders is based at the facility. Devices manufactured by the major pacemaker companies are represented. Adults of all ages are followed, many with complex cardiac problems and arrhythmias. Most patients seen are there for a routine follow-up, but patients with acute problems are also seen. The fellow may also see some of these patients in the emergency department, as an inpatient, or in the operating room. Troubleshooting of acute problems and reprogramming of devices is frequently required.
- The fellow will attend device clinic half a day per week.
- They will work with technicians initially, and as their expertise improves, will have a more independent role in device checks and reprogramming.
- The fellow will see patients in follow-up post device implantation, to evaluate wound healing.
- If a new arrhythmia, device abnormality or end of life parameter is found, the fellow will discuss findings with the EP attending.
- The fellow will also help manage acute device reprogramming issues at times other than their assigned clinic.
- The fellow will discuss new findings with the patient.
An EP attending is available for consultation at all times. Acute problems found in device clinic will be managed by the fellow and attending together.
Device clinic is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. This clinic is overseen by all the EP attendings who implant devices. Since all device problems and changes in device therapy/prescriptions are discussed with an EP attending, the fellow’s progress in device clinic is easily monitored. The fellow is provided with immediate feedback during each case discussion with the attending. Additionally, the fellow receives written semi-annual evaluation from each of the EP device attending. This evaluation is based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellow also receives 360-degree evaluations from patients and device clinic staff, providing feedback on communication skills and their professionalism. In turn, the fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing his evaluations. The fellow evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They also confidentially evaluate the EP attending and EP program director.
The fellow will acquire extensive experience observing wound healing in follow-up of device patients and using pacemaker programming to evaluate and reprogram devices. They will be working alongside and learning from the device technician and nurses. They will learn much technical expertise regarding pacemaker programmers from the technicians.
The EP attending will provide clinical guidance in evaluation of measured data and stored/intracardiac electrograms. The fellow learns by instructing the general cardiology fellows in device evaluation and reprogramming. The fellow also learns by educating patients and their families about changes in their device and heart rhythm status.
Other important methods are self-study and participating in the didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- EKG Conference
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this rotation is to provide the fellow with a meaningful EP research experience and enable the fellow to critically assess medical literature with regard to new therapies and techniques.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Have identified an EP attending as their research mentor and selected a suitable EP-related clinical research project. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Understand steps required for IRB approval, if required for their project. (MK, P, ISC)
- Have presented the proposed project at EP research conference, with the help of their mentor. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Have presented multiple journal articles at EP conferences, critically appraising the data and recommendations, with the assistance of the EP faculty. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Be familiar with the significance of ongoing EP-related multicenter trials Penn State Health faculty are participating in. (PC, MK, PBLI, SBP)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Have completed their research project and analyzed the data. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Have presented findings of the project at EP research conference to receive input from the remainder of the EP faculty and fellows. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Have an abstract written, or planned for submission to a major scientific meeting the following year. It is expected that a manuscript will also be ultimately prepared for publication in a peer-reviewed journal the following year. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- Be able to independently analyze and critique scientific published EP literature to decide whether the information should change their clinical practice. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
The chosen clinical research project can pertain to any of the EP (invasive or noninvasive) procedures or a wide range of arrhythmia problems encountered. Although it is assumed that a clinical project will be chosen, the fellow may decide to work with one of Penn State College of Medicine’s basic scientists in the cardiology department who study the autonomic nervous system. Patients represent adults of all ages and there is an appropriate gender mix. Since the region represented is central Pennsylvania, the patient population is fairly homogenous, but with diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. There are a significant number of patients followed at Hershey Medical Center who have congenital heart disease and cardiomyopathies with heart failure. Multicenter trials mainly pertain to implantable devices or antiarrhythmic drug therapy. The fellow will contact the attending Principal Investigator or research nurse coordinator regarding enrolling one of their patients in a trial. Eligible patients for research studies may come from the inpatient or outpatient setting.
- The fellow will discuss potential research projects with EP faculty, and with their chosen mentor, picking a project that best suit their needs.
- The fellow will perform the required literature search.
- With the help of their EP mentor, the fellow will design a protocol.
- The fellow will participate in obtaining the necessary IRB approval, and preparation of consent forms.
- The fellow will present the proposed research protocol at EP research conference.
- The fellow will take the lead in recruiting patients, obtaining consent, collecting and analyzing data.
- The fellow will discuss findings or problems with their EP research mentor.
- The fellow will present findings of their research project at an EP research conference.
- The fellow will prepare an abstract, using their data, to submit to a major scientific meeting.
- The fellow’s goal should be to write a manuscript for publication based on their acquired data.
- The fellow will identify potential patients for multicenter clinical trials, from the patients they encounter in the inpatient and outpatient settings.
- The fellow is responsible for compiling a portfolio of their written material produced during their training period.
The fellows chosen research mentor will guide and advise throughout the project. Additionally, all EP faculty will provide instruction in the analysis and critical appraisal of scientific papers presented at EP conference. They will also provide input in the preparation of abstracts and manuscripts.
Research is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow’s research mentor is their primary evaluator in this area. However, all the EP attendings will evaluate the fellow’s progress in analyzing assigned scientific articles for EP conference. Immediate feedback is given by the faculty regarding research presentations, abstracts and manuscripts. The fellow receives a written semi-annual evaluation from all the EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They confidentially evaluate the EP attending and program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellow and the EP faculty. Other important methods are self-study, and participating in the didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this conference is to help teach the fellow the principles of sound scientific research.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Have consistently attended EP research conferences. (MK)
- Have presented their proposed research project at one of the conferences, with the help of their mentor. (MK, PBLI, ISC, SBP)
- Be aware of the multicenter trials available for their EP patients. (MK, PBLI, SBP)
- Be aware of the clinical research interests/projects of the EP faculty. (MK, PBLI, SBP)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Have consistently attended research conferences and participated in discussions. (MK, PBLI, ISC, SBP)
- Have presented the findings of their research project. (MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
The chosen clinical research project can pertain to any EP (invasive or noninvasive) procedures or a wide range of arrhythmia problems encountered. Although it is assumed that a clinical project will be chosen, the fellow may decide to work with one of Penn State College of Medicine’s basic scientists in the cardiology department who study the autonomic nervous system. Patients represent adults of all ages and there is an appropriate gender mix. Since the region represented is central Pennsylvania, the patient population is fairly homogenous, but with diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. There are a significant number of patients followed at Hershey Medical Center who have congenital heart disease and cardiomyopathies with heart failure. Multicenter trials mainly pertain to implantable devices or antiarrhythmic drug therapy. The fellow will contact the attending Principal Investigator or research nurse coordinator regarding enrolling one of their patients in a trial. Eligible patients for research studies may come from the inpatient or outpatient setting.
- The fellow will attend EP research conferences; attendance is mandatory.
- The fellow will research and prepare a proposal and present this to the EP group at this conference.
- The fellow will actively participate in the other research conferences, striving to provide useful input to the project of their colleagues.
- The fellow will analyze and present their final research data at the conference.
The EP faculty is present for all research conferences providing constructive input. In the past, this input has proved to be valuable to the success of the fellows research projects, leading to publication.
The EP Research Conference occurs monthly and is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. Although the fellow’s research mentor is their primary evaluator in this area, all the EP attendings provide immediate feedback regarding their presentations at the conference. The fellow receives a written semi-annual evaluation from the EP faculty based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellow performs a self evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They confidentially evaluate the EP attending and EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellow and the EP faculty. Other important methods are self-study and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this conference is to provide the fellow with a solid knowledge base in the subspecialty of Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology.
Objectives
During the course of a year, the fellow will:
- Have some knowledge of all the major topics in CCEP, including basic science. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- The fellow will consistently attend this weekly conference; attendance is mandatory.
- The fellow will read the assigned material prior to the conference and be prepared to actively participate in the discussion.
At least one EP attending will be present at the weekly core conference to help teach and answer questions. Faculty will also be available at other times to discuss questions when they arise.
The Core Curriculum Conference occurs weekly and is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow’s attendance is monitored by the fellowship director. The EP attending can observe, on a weekly basis, the fellow’s improving knowledge based and motivation to learn. Immediate feedback is provided regarding the fellow’s understanding of a particular topic. The fellow also receives a written semi-annual evaluation from all EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They confidentially evaluate the EP attending and EP program director.
This planned course is in a board review format. The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellow, their peers and the EP faculty. Other important methods are self-study of the assigned reference materials, and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this conference is to allow the fellow exposure to and discussion of both the recent and classic important EP literature.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Be able to present and provide a critical analysis of a journal article with guidance by an EP attending. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Have knowledge of the major classic and recent EP articles. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P)
- The EP fellows will all read and critically review the assigned journal club articles prior to the meeting time.
- An EP fellow will be assigned to present and critically analyze each article.
- The fellow will attend all monthly EP Journal Clubs, even if they are not scheduled to present an article.
EP Journal Club is attended by all EP faculty. Generally, a faculty member chooses the article(s) to discuss, and assigns a fellow to review the article. All faculty are provided with a copy of the article several prior to the conference, and are available to address questions with the fellow prior to their presentation. After the fellow’s presentation at conference, the EP attendings present provide instruction and insight regarding the subject matter. This should prompt the fellow to study further and review related articles.
The EP Journal Club is a monthly conference, concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow’s attendance is mandatory and monitored by the EP fellowship director. Over time, the EP attending can observe the fellow’s improving skills in presenting and analyzing articles. Immediate feedback is provided to the fellow at the conference by the EP faculty. The fellow also receives a written semi-annual evaluation from all EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The EP fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation, as well as a confidential evaluation of the EP attending and EP program director. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellows and the EP faculty. The other important methods are self-study of the assigned and related articles, and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this conference is to train fellows to identify potential problems in patient care and find ways to improve patient safety.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- With guidance from an EP attending, be able to identify system problems in patient care and propose a plan to prevent future problems. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be able to independently identify system problems and implement changes to improve the safety of their patients. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, P, SBP)
- The fellow will attend all monthly QI conferences and participate in the discussions to provide solutions to system problems.
- The fellow will present cases at this conference, with the help of an attending involved in the case.
- The fellow’s presentation will include identifying system problems and potential solutions to improve patient safety.
- The presenting fellow will do a literature search to identify the scope of the problem and best practice data with guidelines.
The EP QI conference is attended by all EP faculty. An EP attending will help the fellow chose a case (or problem) to present, and be available to discuss the case with the fellow prior to the conference. The EP faculty will provide constructive input regarding the potential system problem and ways to correct the problem.
The EP QI Conference occurs monthly, concurrently with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow’s attendance is mandatory and monitored by the EP fellowship director. Over time, the EP attending can observe the fellow’s improving skills in identifying system problems and devising a QI plan. Immediate feedback from the EP faculty is provided to the fellow at the conference. The fellow also receives a written semi-annual evaluation from all EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The EP fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation, and completes a confidential evaluation of the EP attendings and EP fellowship director. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellows and the EP faculty. The other important methods utilized are self-study of the assigned cases and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this conference is to train fellows in the clinical and technical concepts required of a practicing CCEP physician.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Be able to discuss with faculty and staff the EP maneuvers required to diagnose arrhythmias. (PC, MK, ISC)
- Choose the appropriate catheter for the case after consultation with faculty. (PC, MK, SBP, ISC)
- Be able to diagnose the arrhythmia based on intracardiac electrograms. (PC, MK)
- Have a basic understanding of the imaging and mapping modalities used in the EP lab. (PC, MK)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Have knowledge of the major classic and recent EP articles.
- Be capable of leading a discussion regarding the diagnostic maneuvers used in each case. (PC, MK, ISC, P)
- Independently choose the diagnostic catheters needed for each case. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Teach colleagues how to interpret intracardiac electrogram. (PC, MK, ISC, P)
- Be able to independently apply information obtained from imaging and mapping modalities used in the EP lab. (PC, MK, PBLI)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
Cases discussed in this conference involve EP studies and ablations of all types of arrhythmias. Patients are referred from a wide region in central Pennsylvania. Many patients have very complex cardiac problems, due to congenital heart diseases or cardiomyopathy. Both adult and pediatric cases are reviewed, with an appropriate gender mix.
- The fellow will attend the weekly conference and actively participate in all case discussions.
- The fellow will ask questions about concepts that are not clear to them.
The EP attending involved in the case typically goes over the data and reviews electrograms with all the fellows in the lab. The faculty member leads the discussion and answers questions and instructs in the interpretation of electrograms.
The Clinical Case Conference occurs weekly and is concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow’s attendance is monitored by the fellowship director. The EP attending can observe, on a weekly basis, the fellow’s improving skills and understanding. Immediate feedback is provided to the fellow regarding their understanding on a particular EP concept. The fellow also receives a written semi-annual evaluation from each of the EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They complete a confidential evaluation of each of the EP attending and the EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellows and the EP faculty. The other important methods are self-study of the assigned cases and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Goal
The purpose of this assignment is to assure the trainee an understanding of the basic EP cellular mechanisms as they relate to clinical practice.
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Have attended the monthly basic EP conferences, and attained an understanding of the articles discussed there. (MK, PBLI)
- Have an understanding of the normal cardiac rhythm, including action potentials and ion channels. (MK)
- Understand the determinants of normal conduction. (MK)
- Know the genesis of tachyarrhythmias. (MK)
- Know antiarrhythmic drug actions. (MK)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Be able to lead discussions of basic EP articles at conference and teach basic EP cellular mechanisms. They should be able to apply this knowledge to clinical practice. (PC, MK, PBLI, ISC, SBP)
- The fellow will read and study the assigned basic EP articles.
- They will help present and teach the material at conferences.
EP faculty are present at all conferences where basic EP topics are discussed. The EP faculty help teach and answer questions. They are also present during EP studies, consults and clinic visits to relate clinical experiences to basic cellular concepts.
The Basic EP Conference occurs monthly and is attended by the EP faculty. The fellows attendance is monitored by the fellowship director. The EP attending can monitor, over time, the fellows developing understanding of basic EP principles. At the other conferences, EP clinic, consults, and during analysis of EP study intracardiac electrograms, the attending can observe how the fellow applies these concepts to their clinical decisions. The fellow receives immediate feedback on their understanding on a particular EP concept. The fellow also receives a written semi-annual evaluation from each of the EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They complete a confidential evaluation of each of the EP attending and the EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellows and the EP faculty. The other important methods are self-study and participation in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Objectives
By the end of six months, the fellow should:
- Be adept at interpreting EKGs with complex arrhythmias. (PC, MK)
- Understand the indications for ordering noninvasive studies, including Holter monitors, loop recorders and tilt table testing. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Be able to interpret data obtained from noninvasive EP testing, with the aid of the EP attendings. (PC, MK, ISC)
By the end of 12 months, the fellow should:
- Have taught an EKG conference for the general cardiology fellows. (PC, MK, ISC)
- Understand the protocol and be capable of independently conducting tilt table tests. (PC, MK, PBLI)
- Be able to independently interpret data obtained from noninvasive EP testing and make therapeutic decisions based on the results. (PC, MK, PBLI)
Procedures/Patient Characteristics/Disease Mix/Types of Encounters
We have a dedicated space and staff for the tilt table testing. A specialized tilt table and Finapress monitor is used. Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center offers a variety of ambulatory monitoring services, including Holters and loop recorders. (King of Hearts, Cardionet) The EP service analyzes the tracings. These tests may be ordered by any inpatient service, emergency department physician or through any Penn State-sponsored clinics in the region. The full spectrum of electrophysiologic disorders are represented. There is an appropriate gender mix and adults of all ages are represented. Most patients have some form of insurance. Since the region represented is central Pennsylvania, the patient population is fairly homogenous, but with diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Patients are commonly being evaluated for the effect of antiarrhythmic drug therapy or etiology of syncope or palpitations.
- The fellow will review all EKGs of patients they are seeing in consult and in the clinic.
- The fellow will review the ambulatory monitor tracings of their consult and clinic patients.
- The fellow will participate in tilt table tests when possible.
The fellow will discuss with the attending whether a particular diagnostic noninvasive test is indicated prior to ordering the test. After first reviewing the noninvasive study, the fellow will discuss results and therapeutic plan with an EP attending.
The noninvasive EP rotation runs concurrent with the other fellowship assignments throughout the 12-month training period. The fellow is supervised by the EP attending and their skill can be observed over time by all EP faculty. The fellow is provided with immediate feedback during each discussion with the attending regarding the study data or resultant therapeutic plan. Additionally, the fellow receives a written semi-annual evaluation from each of the EP faculty, based on the ACGME core competencies. The fellowship director then meets with the fellow to discuss their progress. The fellow performs a self-evaluation after reviewing their evaluations. The fellow also evaluates and provides input to the curriculum. They complete a confidential evaluation of each of the EP attending and the EP program director.
The primary teaching method employed is tutorial between the fellows and the EP attending. Also, the fellow learns by teaching general cardiology fellows, medicine residents and medical students. The other important methods are self-study and participating in the other didactic sessions listed below.
Didactic Sessions
- Journal Club
- Research Conference
- Basic Science Conference
- M and M (QI) Conferences (EP and HVI)
- Clinical Case Conference
- Core Curriculum Conference
- Medicine Core Competency Conferences
- Cardiology and HVI Grand Rounds
Textbooks
- Zipes and Jalife: Cardiac Electrophysiology from Cell to Bedside. WB Saunders
- Josephson: Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology. Lippincott
- Chou: Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice. Saunders
- Pacing Textbooks
Journals
- Heart Rhythm
- Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology (JCE)
- Journal of Interventional Cardiovascular Electrophysiology (JICE)
- Pacing and Cardiac Electrophysiology (PACE)
- All articles assigned for EP conferences
Websites
Latest News from the Heart and Vascular Institute







